Authorization Rules
Authorization rules define who can do what on which resources, and under which conditions.
They are the foundation of your access control policy in Big ACL.
Big ACL analyzes your rules, validates them against your data model, and enforces them across your applications.
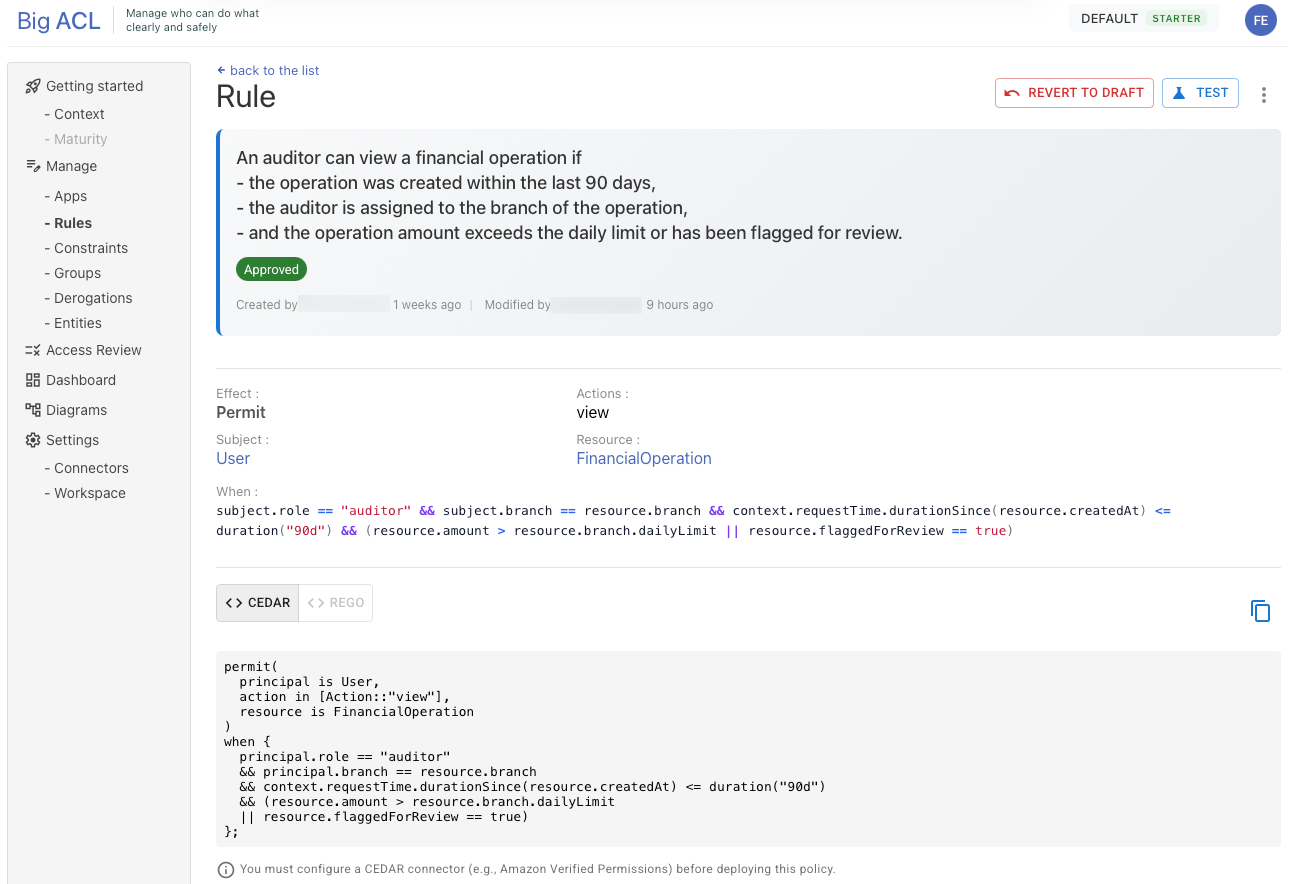
The Rule Structure
Section titled “The Rule Structure”Every rule follows a simple pattern:
[Principal] can [Action] on [Resource] if [Conditions]
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Principal | Who is requesting access (user, service, role) |
| Action | What they want to do (read, write, delete, approve) |
| Resource | What they want to access (document, account, order) |
| Conditions | When the access is allowed (optional constraints) |
Writing Effective Rules
Section titled “Writing Effective Rules”Start with Natural Language
Section titled “Start with Natural Language”Write your rules as clear, complete sentences that describe your business policy:
- “A developer can access a repository if they belong to the same team as the repository owner.”
- “A manager can approve expenses if the amount is below their approval limit.”
- “A back-office user can validate a financial operation if they have the manager role and the operation is linked to their branch.”
Keep Rules Atomic
Section titled “Keep Rules Atomic”Each rule should express a single access decision. If a rule becomes complex or hard to understand, split it into multiple simpler rules.
Instead of:
“A user can read, write, and delete documents if they are the owner, or read documents if they are in the same department.”
Write:
“A user can read, write, and delete documents if they are the owner.”
“A user can read documents if they belong to the same department.”
Be Specific
Section titled “Be Specific”Avoid vague or ambiguous language. Clearly identify the subjects, resources, and conditions.
Avoid:
“Users can access stuff when appropriate.”
Prefer:
“An employee can view salary information if they are viewing their own record.”
Rule Components
Section titled “Rule Components”Effect
Section titled “Effect”The effect determines whether the rule grants or denies access:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Permit | Allows the action when conditions are met |
| Deny | Blocks the action when conditions are met |
By default, access is denied unless explicitly permitted. Use Deny rules to create exceptions to broader Permit rules.
Principal (Subject)
Section titled “Principal (Subject)”The subject is the entity requesting access. In Big ACL, subjects are defined in your data model and typically represent:
- Users or employees
- Service accounts
- Applications or systems
- Roles or groups
You can optionally restrict a rule to specific subject groups (e.g., “Managers”, “External contractors”).
Resource
Section titled “Resource”The resource is what the subject wants to access. Resources are also defined in your data model and can represent:
- Documents or files
- Database records
- Application features
- Business objects (orders, invoices, accounts)
You can optionally restrict a rule to specific resource groups (e.g., “Confidential documents”, “Production systems”).
Actions
Section titled “Actions”Actions define what operations are allowed or denied on the resource. Actions are specific to each resource type and defined in your data model.
Common examples:
- Documents: read, write, delete, share
- Orders: view, create, approve, cancel
- Accounts: view, edit, transfer, close
A single rule can grant multiple actions at once.
Conditions
Section titled “Conditions”Conditions add context-based constraints to your rules. They are optional but powerful.
When Conditions
Section titled “When Conditions”“When” conditions specify requirements that must be true for the rule to apply:
- “when the user belongs to the same department as the document owner”
- “when the amount is below the user’s approval limit”
- “when the request is made during business hours”
Unless Conditions
Section titled “Unless Conditions”“Unless” conditions specify exceptions that prevent the rule from applying:
- “unless the document is marked as confidential”
- “unless the user’s account is suspended”
- “unless the resource is archived”
Rule Lifecycle
Section titled “Rule Lifecycle”Rules follow a structured lifecycle to ensure proper review and governance before they are enforced.
Statuses
Section titled “Statuses”| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Draft | The rule is being written and analyzed. You can edit and test it freely. |
| Proposed | The rule has been submitted for review. Waiting for approval. |
| Approved | The rule has been approved and is ready for deployment. |
| Enforced | The rule is active and making access decisions in your applications. |
| Suspended | The rule has been temporarily disabled. It can be reactivated. |
| Archived | The rule is no longer active and is kept for historical reference. |
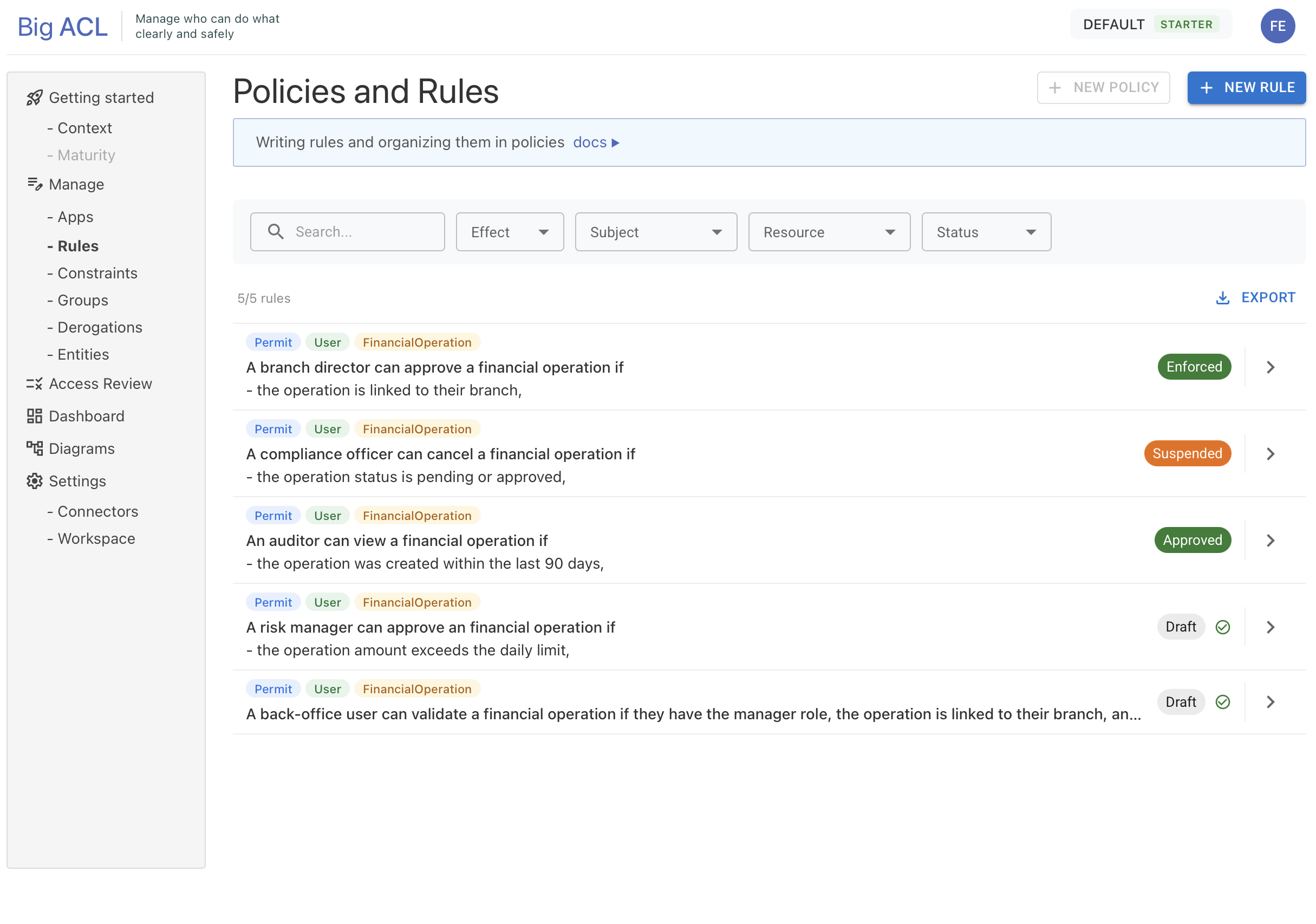
Workflow
Section titled “Workflow”The rule lifecycle depends on your subscription plan:
Starter Plan (Single User)
Section titled “Starter Plan (Single User)”For individual users or small teams, the workflow is simplified:
Draft → Approved → Enforced- Click Validate to approve your rule directly
- The rule is ready for deployment once approved
Enterprise Plan (Team Collaboration)
Section titled “Enterprise Plan (Team Collaboration)”For teams requiring review and approval:
Draft → Proposed → Approved → Enforced- Submit for Review: Send the rule to be reviewed by a team member
- Approve or Reject: A reviewer can approve the rule or reject it back to Draft
- Deploy: Approved rules are deployed to your policy engine
Available Actions by Status
Section titled “Available Actions by Status”| Status | Available Actions |
|---|---|
| Draft | Edit, Test, Validate/Submit for Review, Archive, Delete |
| Proposed | Approve, Reject, Test, Archive |
| Approved | Revert to Draft, Test, Archive |
| Enforced | Suspend, Test, Archive |
| Suspended | Reactivate, Revert to Draft, Test, Archive |
| Archived | Restore, Delete |
Reverting Rules
Section titled “Reverting Rules”You can revert a rule back to Draft status from the following states:
- Proposed: If the rule needs changes before approval
- Approved: If you need to make modifications before deployment
- Suspended: If you want to edit a suspended rule
When reverting to Draft, the rule will need to go through the approval process again.
Suspending and Reactivating
Section titled “Suspending and Reactivating”If an enforced rule is causing issues, you can Suspend it temporarily without archiving. This allows you to:
- Quickly disable a problematic rule
- Investigate the issue
- Reactivate the rule when ready, or
- Revert to Draft to make changes
Deleting Rules
Section titled “Deleting Rules”Rules can only be deleted when in Draft or Archived status. This protects active rules from accidental deletion.
Analysis
Section titled “Analysis”When you create or modify a rule, Big ACL automatically analyzes it:
- Parsing: Validates the rule syntax and structure
- Entity Resolution: Maps subjects and resources to your data model
- Conflict Detection: Identifies potential conflicts with other rules
- Test Generation: Suggests test cases to validate the rule behavior
During analysis:
- The rule cannot be edited
- An analysis status indicator displays the current state:
PENDING,COMPLETE, orERROR - A status badge is also visible in the policy’s rule grid (Authoring Zone)
- Review any warnings or suggestions before submitting for review
Editing Rules
Section titled “Editing Rules”Big ACL offers several ways to modify existing rules:
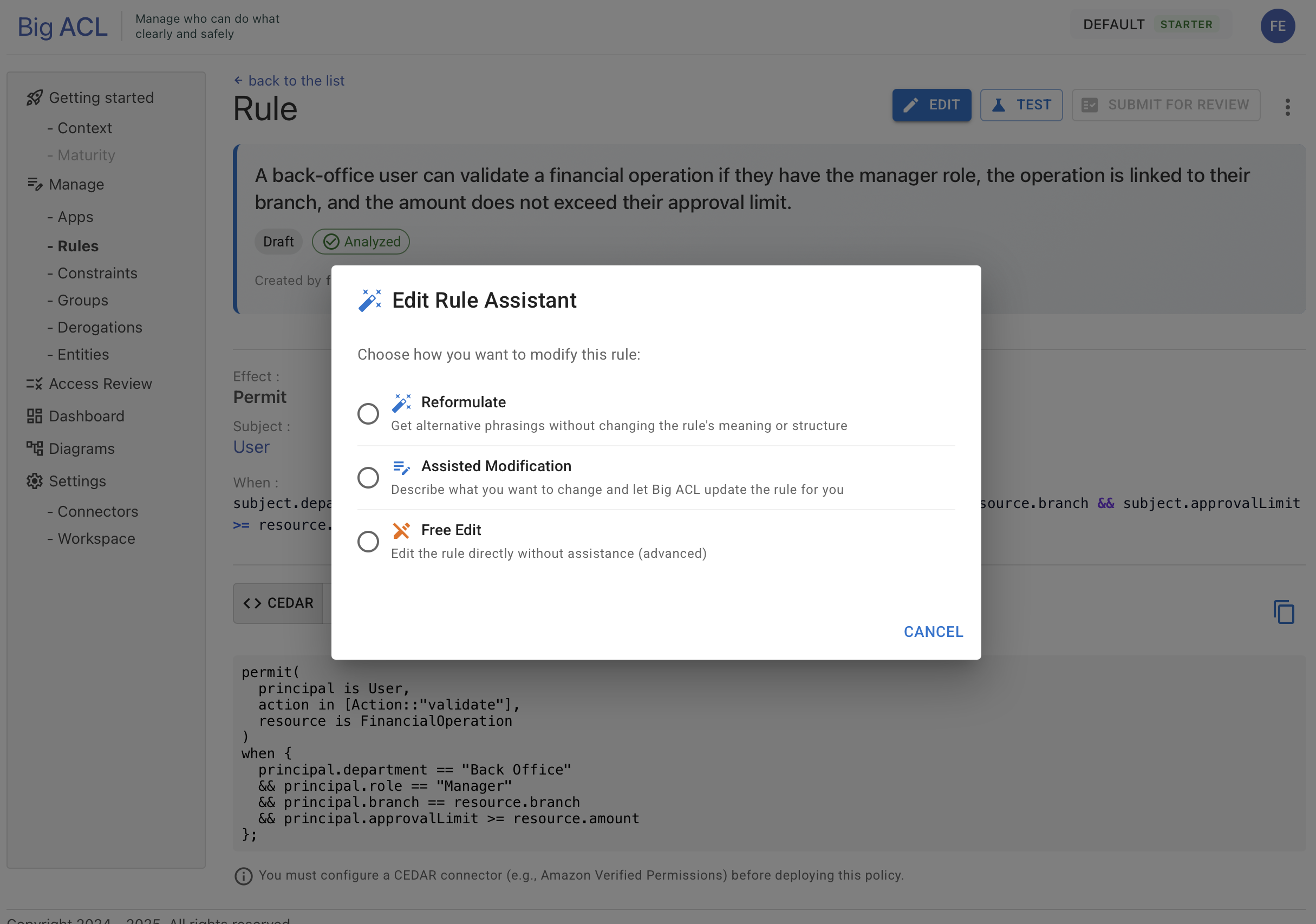
Rule Edit Assistant
Section titled “Rule Edit Assistant”An AI assistant is integrated into the rule editor. It can analyze your rule in context and suggest improvements, identify potential issues, or help you refine conditions based on your data model.
Reformulate
Section titled “Reformulate”Get alternative phrasings for your rule without changing its meaning. Useful when you want to:
- Improve clarity
- Standardize terminology
- Make the rule easier to understand
Assisted Modification
Section titled “Assisted Modification”Describe what you want to change in natural language, and Big ACL will update the rule for you. Examples:
- “Add the delete action”
- “Restrict to managers only”
- “Add a condition requiring department match”
Free Edit
Section titled “Free Edit”Directly modify all rule components. Recommended for advanced users who understand the full rule structure.
Testing Rules
Section titled “Testing Rules”Tests are now run at the policy level, in the Verify Panel. See Testing your Policy for details.
Best Practices
Section titled “Best Practices”Naming and Description
Section titled “Naming and Description”Write clear descriptions that explain the business intent:
- Good: “A developer can push code to a repository if they are a member of the repository’s team and the branch is not protected.”
- Poor: “Dev repo access rule”
Start Simple
Section titled “Start Simple”Begin with broad permit rules, then add specific deny rules for exceptions:
- “Employees can view company documents.”
- “Employees cannot view documents marked as board-confidential unless they are a board member.”
Use Groups
Section titled “Use Groups”Organize subjects and resources into groups to simplify rule management:
- Instead of listing individual users, reference groups like “Finance team” or “Senior managers”
- Group resources by sensitivity level or business domain
Test Before Enforcement
Section titled “Test Before Enforcement”Always validate rules with test cases before setting them to Enforced status. Consider:
- Normal use cases (should be permitted)
- Edge cases (verify correct handling)
- Security scenarios (should be denied)
Regular Review
Section titled “Regular Review”Periodically review your rules to ensure they:
- Remain aligned with current business policies
- Reflect organizational changes (new roles, departments)
- Don’t contain obsolete references
Organizing Rules with Policies
Section titled “Organizing Rules with Policies”Rules are organized within policies — containers that group authorization rules by business domain. For more information, see the Policies page.
Getting Started
Section titled “Getting Started”- Navigate to Policies in the Big ACL console
- Open or create a policy
- Click “Add Rule” in the Authoring Zone to open the multi-step creation editor
- Write your rule as a clear, complete sentence (minimum 4 words)
- Review the analysis to ensure the rule is valid
- Test your policy using the Verify Panel
- Set to Enforced when ready to activate